Companies that can generate consistent earnings, such as many utility companies, may carry more debt on the balance sheet. Lenders are interested in the number of times a business can increase earnings without taking on more debt, and this situation improves the TIE ratio. A company’s financial health depends on the total amount of debt, and the current income (earnings) the firm can generate. The times interest earned formula is EBIT (company’s earnings before interest and taxes) divided by total interest expense on debt. Debts may include notes payable, lines of credit, and interest obligations on bonds. You also learned about what a good asset turnover ratio is, how to use them to analyze companies and more.
How Can a Company Improve Its Asset Turnover Ratio?
Using total assets reflects management’s decisions on all capital expenditures and other assets. In simple terms, the asset turnover ratio means how much revenue you earn based on the total assets. And this revenue figure would equate to the sales figure in your Income Statement. The higher the number the better would be the asset efficiency of the organization. It’s being seen that in the retail industry, this ratio is usually higher, i.e., more than 2. Negative asset turnover indicates that a company’s sales are less than its average total assets.
Example Calculation of Asset Turnover
This article explores the times interest earned (TIE) ratio, provides several examples of its application, and explains how your business can improve the ratio’s value over time. To improve a low ATR, a company can take measures like stocking popular items, restocking inventory when needed, and extending operating hours to attract more customers and boost sales. As everything has its good and bad sides, the asset turnover ratio has two things that make this ratio limited in scope. Of course, it helps us understand the asset utility in the organization, but this ratio has two shortcomings that we should mention.
Calculating Total Assets
- Rho’s AP automation helps process payables in a single workflow — from invoice to payment — with integrated accounting, and Rho fully automates expense management.
- Check out our debt to asset ratio calculator and fixed asset turnover ratio calculator to understand more on this topic.
- The asset turnover ratio is most useful when compared across similar companies.
- The total asset turnover ratio should be used in combination with other financial ratios for a comprehensive analysis.
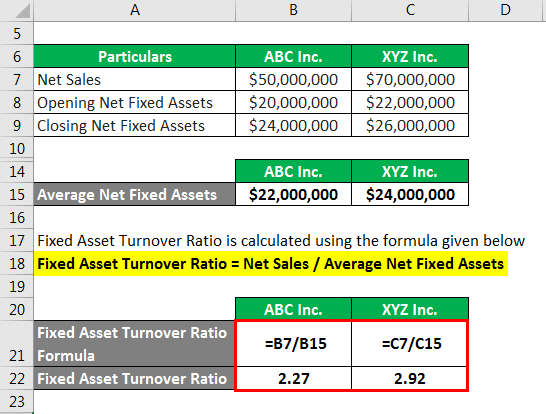
- The fixed asset turnover ratio (FAT ratio) is used by analysts to measure operating performance.
A higher ATR signifies a company’s exceptional ability to generate significant revenue using a relatively smaller pool of assets. For optimal use, it is best employed for comparing companies within the same industry, providing valuable insights into their operational efficiency and revenue generation capabilities. A higher ratio is generally favored as there is the implication that the company is more efficient in generating sales or revenues. A lower ratio illustrates that a company may not be using its assets as efficiently. Asset turnover ratios vary throughout different sectors, so only the ratios of companies that are in the same sector should be compared.
Formula for Asset Turnover Ratio
Review all of the costs you incur, and identify areas where costs can be reduced. If you can purchase a product through multiple suppliers, you can force the suppliers to compete for your business and offer lower prices. Access all first party information such as slide decks, transcripts, and earnings reports from public companies worldwide in one convenient platform. • Accounts receivable are accounts that hold expected revenues that come from when customers use credit to buy goods and services.
Fixed ATR
Fixed asset turnover and asset turnover are two different ratios that can tell you about a company, and for investors, it’s important to understand the difference between the two. For instance, other ratios that can be used to gain an understanding of a company’s financials are the debt-to-equity ratio, its P/E ratio, and even looking at its net asset value. Although having cash on hand is important for growing and maintaining a business, other types of business assets are also important, as is how a company chooses to use them. Liquid assets can include cash, stock, and anything else the company owns that could be easily liquidated into cash. Fixed assets are things the company owns that are not as easily turned into cash.
On the flip side, a turnover ratio far exceeding the industry norm could be an indication that the company should be spending more and might be falling behind in terms of development. Successful businesses have a formal process to follow up on late payments. For example, your firm may email customers when an invoice is 30 days old and call clients if an invoice reaches 45 days old. Non-responsive customers should be sent to collections for more follow-up.
Understand the qualitative aspects of entire industries or specific companies. Eliminate hours of searching for specific data points buried deep inside company material. Interpretation of the Asset Turnover the asset turnover ratio is calculated as net sales divided by Ratio is highly industry-dependent. What may be considered a “good” ratio in one industry may be viewed as poor in another. This is because asset intensity can greatly differ among different industries.
The ratio is typically calculated on an annual basis, though any time period can be selected. Asset turnover ratios differ between industry sectors, making it crucial to compare only companies within the same sector. For instance, retail or service sector companies typically have smaller asset bases but generate higher sales volumes, resulting in higher average asset turnover ratios. Manufacturing companies often favor the FAT ratio over the asset turnover ratio to determine how well capital investments perform. Companies with fewer fixed assets such as retailers may be less interested in the FAT compared to how other assets such as inventory are utilized.
To calculate the ratio, locate earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) in the multi-step income statement, and interest expense. A multi-step income statement provides more detail than a traditional income statement, and includes EBIT. But even if your asset turnover ratio number isn’t where you want it to be, don’t worry—that number isn’t set in stone.
Asset turnover ratio measures how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate sales, while return on assets (ROA) measures how effectively it uses its assets to generate profits. The asset turnover ratio measures operational efficiency, while ROA reflects operational efficiency and profitability. Sometimes investors also want to see how companies use more specific assets like fixed assets and current assets. The fixed asset turnover ratio and the working capital ratio are turnover ratios similar to the asset turnover ratio that are often used to calculate the efficiency of these asset classes.
